Housing Affordability Continued to Improve in August
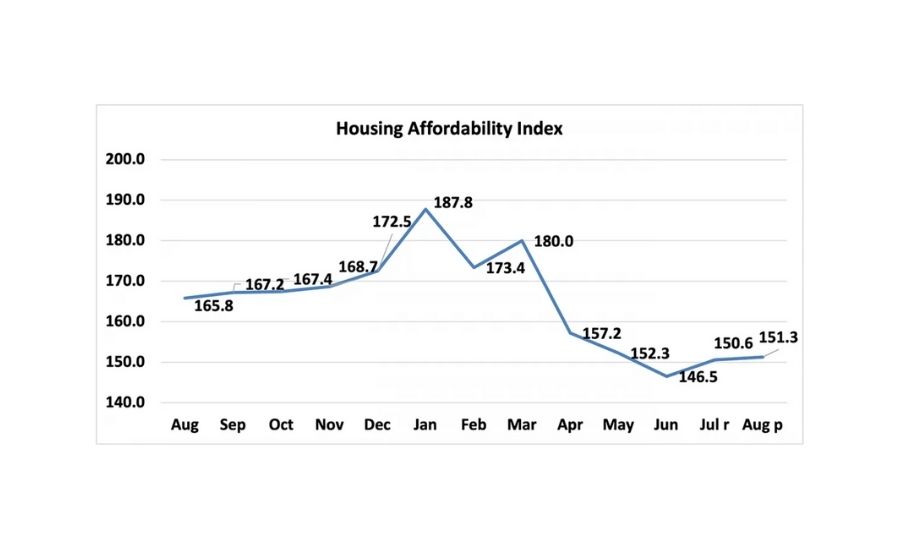
The Housing Affordability Index calculation assumes a 20% down payment and a 25% qualifying ratio (principal and interest payment to income). Chart: National Association of Realtors.
At the national level, housing affordability increased for the second consecutive month in August compared to the previous month according to National Association of Realtors Housing Affordability Index. Compared to the prior month, affordability improved as the monthly mortgage payment fell by 1.1% while the median family income fell modestly by 0.7%.
Compared to one year ago, affordability declined in August as the median family income rose by 3.9% while the monthly mortgage payment increased 13.9%. The effective 30-year fixed mortgage rate was 2.89% this August compared to 3.00% one year ago, and the median existing-home sales price rose 15.6% from one year ago.
As of August 2021, the national and regional indices were all above 100, meaning that a family with the median income had more than the income required to afford a median-priced home. The income required to afford a mortgage, or the qualifying income, is the income needed so that mortgage payments on a 30-year fixed mortgage loan with 20% down payment account for 25% of family income. The most affordable region was the Midwest, with an index value of 196.8 (median family income of $86,614 with the qualifying income of $44,016). The least affordable region remained the West, where the index was 114.9 (median family income of $94,372 and the qualifying income of $82,128). The South was the second most affordable region with an index of 160.6 (median family income of $80,180 and the qualifying income of $49,920) The Northeast was the second most unaffordable region with an index of 149.1 (median family income of $99,286 with a qualifying income of $66,576).
Housing affordability declined from a year ago in all the four regions. The Northeast had the biggest decline of 10.7%. The South region experienced a weakening in price growth compared to a year ago of 7.1% followed by the West with a dip of 4.9%. The Midwest had the smallest decrease of 4.8%.
For more information, visit nar.realtor.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






